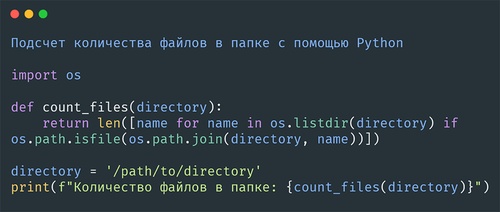
Получаем доступ к документации с помощью функции help() в Python
- 14.04.2023
- 665
- Основы Python
- Функции
Функция
help()является встроенной функцией Python, которая предоставляет доступ к документации и информации о функциях, методах, модулях, классах и объектах.
Эта функция может быть очень полезна при изучении новых библиотек или работе с неизвестными объектами и методами, поскольку позволяет получить информацию о них прямо в интерпретаторе Python.
Синтаксис
Синтаксис функции help() следующий:
help(object)object: Объект, о котором требуется получить информацию. Это может быть функция, метод, модуль, класс или переменная.
Получение информации о функциях и методах
Функция help() может быть использована для получения информации о встроенных и пользовательских функциях или методах.
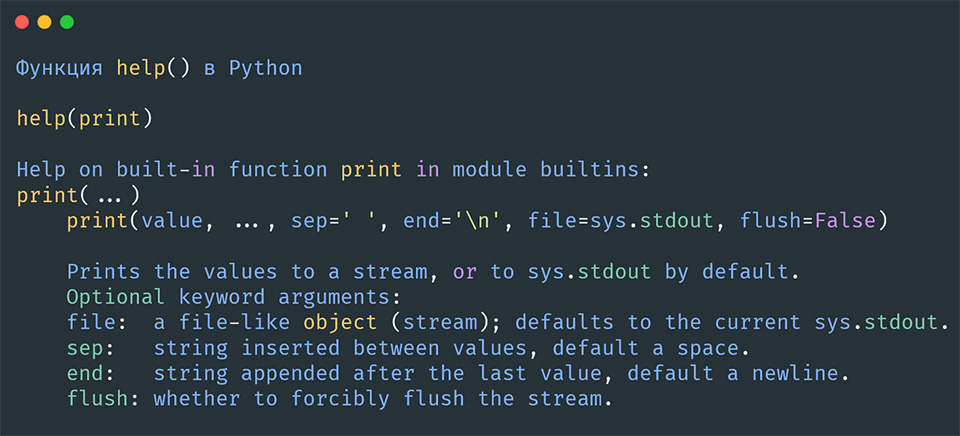
Пример 1: Получение информации о встроенной функции print()
help(print)Результат:
Help on built-in function print in module builtins:
print(...)
print(value, ..., sep=' ', end='\n', file=sys.stdout, flush=False)
Prints the values to a stream, or to sys.stdout by default.
Optional keyword arguments:
file: a file-like object (stream); defaults to the current sys.stdout.
sep: string inserted between values, default a space.
end: string appended after the last value, default a newline.
flush: whether to forcibly flush the stream.Пример 2: Получение информации о пользовательской функции
def example_function(a, b):
"""
Returns the sum of a and b.
Args:
a: First number
b: Second number
Returns:
The sum of a and b.
"""
return a + b
help(example_function)Результат:
Help on function example_function in module __main__:
example_function(a, b)
Returns the sum of a and b.
Args:
a: First number
b: Second number
Returns:
The sum of a and b.Получение информации о модулях
Функция help() также может быть использована для получения информации о модулях, включая встроенные и сторонние модули.
Пример 3: Получение информации о модуле math
import math
help(math)Результат
Help on built-in module math:
NAME
math
DESCRIPTION
This module provides access to the mathematical functions
defined by the C standard.
FUNCTIONS
acos(x, /)
Return the arc cosine (measured in radians) of x.
The result is between 0 and pi.
acosh(x, /)
Return the inverse hyperbolic cosine of x.
asin(x, /)
Return the arc sine (measured in radians) of x.
The result is between -pi/2 and pi/2.
asinh(x, /)
Return the inverse hyperbolic sine of x.
atan(x, /)
Return the arc tangent (measured in radians) of x.
The result is between -pi/2 and pi/2.
atan2(y, x, /)
Return the arc tangent (measured in radians) of y/x.
Unlike atan(y/x), the signs of both x and y are considered.
atanh(x, /)
Return the inverse hyperbolic tangent of x.
ceil(x, /)
Return the ceiling of x as an Integral.
This is the smallest integer >= x.
comb(n, k, /)
Number of ways to choose k items from n items without repetition and without order.
Evaluates to n! / (k! * (n - k)!) when k <= n and evaluates
to zero when k > n.
Also called the binomial coefficient because it is equivalent
to the coefficient of k-th term in polynomial expansion of the
expression (1 + x)**n.
Raises TypeError if either of the arguments are not integers.
Raises ValueError if either of the arguments are negative.
copysign(x, y, /)
Return a float with the magnitude (absolute value) of x but the sign of y.
On platforms that support signed zeros, copysign(1.0, -0.0)
returns -1.0.
cos(x, /)
Return the cosine of x (measured in radians).
cosh(x, /)
Return the hyperbolic cosine of x.
degrees(x, /)
Convert angle x from radians to degrees.
dist(p, q, /)
Return the Euclidean distance between two points p and q.
The points should be specified as sequences (or iterables) of
coordinates. Both inputs must have the same dimension.
Roughly equivalent to:
sqrt(sum((px - qx) ** 2.0 for px, qx in zip(p, q)))
erf(x, /)
Error function at x.
erfc(x, /)
Complementary error function at x.
exp(x, /)
Return e raised to the power of x.
expm1(x, /)
Return exp(x)-1.
This function avoids the loss of precision involved in the direct evaluation of exp(x)-1 for small x.
fabs(x, /)
Return the absolute value of the float x.
factorial(x, /)
Find x!.
Raise a ValueError if x is negative or non-integral.
floor(x, /)
Return the floor of x as an Integral.
This is the largest integer <= x.
fmod(x, y, /)
Return fmod(x, y), according to platform C.
x % y may differ.
frexp(x, /)
Return the mantissa and exponent of x, as pair (m, e).
m is a float and e is an int, such that x = m * 2.**e.
If x is 0, m and e are both 0. Else 0.5 <= abs(m) < 1.0.
fsum(seq, /)
Return an accurate floating point sum of values in the iterable seq.
Assumes IEEE-754 floating point arithmetic.
gamma(x, /)
Gamma function at x.
gcd(*integers)
Greatest Common Divisor.
hypot(...)
hypot(*coordinates) -> value
Multidimensional Euclidean distance from the origin to a point.
Roughly equivalent to:
sqrt(sum(x**2 for x in coordinates))
For a two dimensional point (x, y), gives the hypotenuse
using the Pythagorean theorem: sqrt(x*x + y*y).
For example, the hypotenuse of a 3/4/5 right triangle is:
>>> hypot(3.0, 4.0)
5.0
isclose(a, b, *, rel_tol=1e-09, abs_tol=0.0)
Determine whether two floating point numbers are close in value.
rel_tol
maximum difference for being considered "close", relative to the
magnitude of the input values
abs_tol
maximum difference for being considered "close", regardless of the
magnitude of the input values
Return True if a is close in value to b, and False otherwise.
For the values to be considered close, the difference between them
must be smaller than at least one of the tolerances.
-inf, inf and NaN behave similarly to the IEEE 754 Standard. That
is, NaN is not close to anything, even itself. inf and -inf are
only close to themselves.
isfinite(x, /)
Return True if x is neither an infinity nor a NaN, and False otherwise.
isinf(x, /)
Return True if x is a positive or negative infinity, and False otherwise.
isnan(x, /)
Return True if x is a NaN (not a number), and False otherwise.
isqrt(n, /)
Return the integer part of the square root of the input.
lcm(*integers)
Least Common Multiple.
ldexp(x, i, /)
Return x * (2**i).
This is essentially the inverse of frexp().
lgamma(x, /)
Natural logarithm of absolute value of Gamma function at x.
log(...)
log(x, [base=math.e])
Return the logarithm of x to the given base.
If the base not specified, returns the natural logarithm (base e) of x.
log10(x, /)
Return the base 10 logarithm of x.
log1p(x, /)
Return the natural logarithm of 1+x (base e).
The result is computed in a way which is accurate for x near zero.
log2(x, /)
Return the base 2 logarithm of x.
modf(x, /)
Return the fractional and integer parts of x.
Both results carry the sign of x and are floats.
nextafter(x, y, /)
Return the next floating-point value after x towards y.
perm(n, k=None, /)
Number of ways to choose k items from n items without repetition and with order.
Evaluates to n! / (n - k)! when k <= n and evaluates
to zero when k > n.
If k is not specified or is None, then k defaults to n
and the function returns n!.
Raises TypeError if either of the arguments are not integers.
Raises ValueError if either of the arguments are negative.
pow(x, y, /)
Return x**y (x to the power of y).
prod(iterable, /, *, start=1)
Calculate the product of all the elements in the input iterable.
The default start value for the product is 1.
When the iterable is empty, return the start value. This function is
intended specifically for use with numeric values and may reject
non-numeric types.
radians(x, /)
Convert angle x from degrees to radians.
remainder(x, y, /)
Difference between x and the closest integer multiple of y.
Return x - n*y where n*y is the closest integer multiple of y.
In the case where x is exactly halfway between two multiples of
y, the nearest even value of n is used. The result is always exact.
sin(x, /)
Return the sine of x (measured in radians).
sinh(x, /)
Return the hyperbolic sine of x.
sqrt(x, /)
Return the square root of x.
tan(x, /)
Return the tangent of x (measured in radians).
tanh(x, /)
Return the hyperbolic tangent of x.
trunc(x, /)
Truncates the Real x to the nearest Integral toward 0.
Uses the __trunc__ magic method.
ulp(x, /)
Return the value of the least significant bit of the float x.
DATA
e = 2.718281828459045
inf = inf
nan = nan
pi = 3.141592653589793
tau = 6.283185307179586
FILE
(built-in)Получение информации об объектах
Функция help() может быть использована для получения информации об объектах различных типов, таких как списки, кортежи, словари и т. д.
Пример 4: Получение информации о списке
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
help(my_list)Результат:
Help on list object:
class list(object)
| list(iterable=(), /)
|
| Built-in mutable sequence.
|
| If no argument is given, the constructor creates a new empty list.
| The argument must be an iterable if specified.
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __add__(self, value, /)
| Return self+value.
|
| __contains__(self, key, /)
| Return key in self.
|
| __delitem__(self, key, /)
| Delete self[key].
|
| __eq__(self, value, /)
| Return self==value.
|
| __ge__(self, value, /)
| Return self>=value.
|
| __getattribute__(self, name, /)
| Return getattr(self, name).
|
| __getitem__(...)
| x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y]
|
| __gt__(self, value, /)
| Return self>value.
|
| __iadd__(self, value, /)
| Implement self+=value.
|
| __imul__(self, value, /)
| Implement self*=value.
|
| __init__(self, /, *args, **kwargs)
| Initialize self. See help(type(self)) for accurate signature.
|
| __iter__(self, /)
| Implement iter(self).
|
| __le__(self, value, /)
| Return self<=value.
|
| __len__(self, /)
| Return len(self).
|
| __lt__(self, value, /)
| Return self<value.
|
| __mul__(self, value, /)
| Return self*value.
|
| __ne__(self, value, /)
| Return self!=value.
|
| __repr__(self, /)
| Return repr(self).
|
| __reversed__(self, /)
| Return a reverse iterator over the list.
|
| __rmul__(self, value, /)
| Return value*self.
|
| __setitem__(self, key, value, /)
| Set self[key] to value.
|
| __sizeof__(self, /)
| Return the size of the list in memory, in bytes.
|
| append(self, object, /)
| Append object to the end of the list.
|
| clear(self, /)
| Remove all items from list.
|
| copy(self, /)
| Return a shallow copy of the list.
|
| count(self, value, /)
| Return number of occurrences of value.
|
| extend(self, iterable, /)
| Extend list by appending elements from the iterable.
|
| index(self, value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)
| Return first index of value.
|
| Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
|
| insert(self, index, object, /)
| Insert object before index.
|
| pop(self, index=-1, /)
| Remove and return item at index (default last).
|
| Raises IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range.
|
| remove(self, value, /)
| Remove first occurrence of value.
|
| Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
|
| reverse(self, /)
| Reverse *IN PLACE*.
|
| sort(self, /, *, key=None, reverse=False)
| Sort the list in ascending order and return None.
|
| The sort is in-place (i.e. the list itself is modified) and stable (i.e. the
| order of two equal elements is maintained).
|
| If a key function is given, apply it once to each list item and sort them,
| ascending or descending, according to their function values.
|
| The reverse flag can be set to sort in descending order.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Class methods defined here:
|
| __class_getitem__(...) from builtins.type
| See PEP 585
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Static methods defined here:
|
| __new__(*args, **kwargs) from builtins.type
| Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data and other attributes defined here:
|
| __hash__ = NoneПолучение информации о классах
Функция help() также может быть использована для получения информации о классах и их методах.
Пример 5: Получение информации о пользовательском классе
class ExampleClass:
"""
This is an example class.
Attributes:
attr1: An attribute that stores a value.
"""
def __init__(self, attr1):
"""
Initializes the ExampleClass with the given attribute value.
Args:
attr1: The value of the attribute.
"""
self.attr1 = attr1
def get_attr1(self):
"""
Returns the value of attr1.
Returns:
The value of attr1.
"""
return self.attr1
help(ExampleClass)Результат:
Help on class ExampleClass in module __main__:
class ExampleClass(builtins.object)
| ExampleClass(attr1)
|
| This is an example class.
|
| Attributes:
| attr1: An attribute that stores a value.
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __init__(self, attr1)
| Initializes the ExampleClass with the given attribute value.
|
| Args:
| attr1: The value of the attribute.
|
| get_attr1(self)
| Returns the value of attr1.
|
| Returns:
| The value of attr1.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors defined here:
|
| __dict__
| dictionary for instance variables (if defined)
|
| __weakref__
| list of weak references to the object (if defined)
Process finished with exit code 0
Заключение
Мы рассмотрели функцию help(), которая предоставляет доступ к документации и информации о функциях, методах, модулях, классах и объектах. Изучили основной синтаксис этой функции и привели различные примеры ее использования, такие как получение информации о встроенных и пользовательских функциях, модулях, объектах и классах. Функция help() является полезным инструментом для изучения новых библиотек или работы с неизвестными объектами и методами, поскольку позволяет получать информацию о них прямо в интерпретаторе Python.
Содержание: